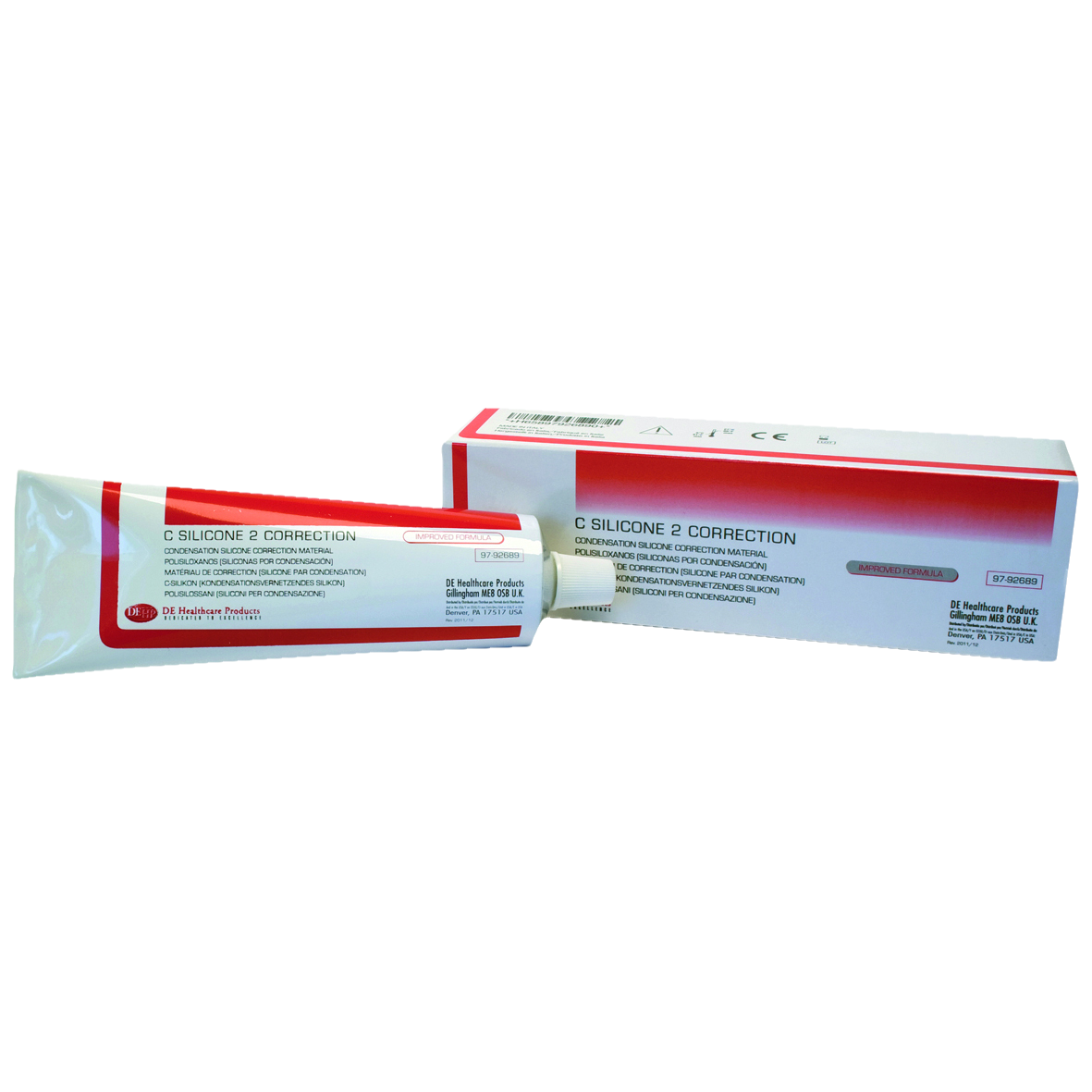
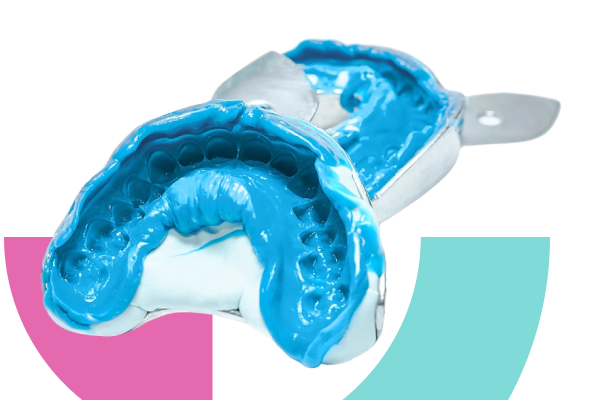
Silicone is one of the most widely used impression materials for fixed and removable dental prostheses, such as crowns and bridges. There are two main types of silicone impression. These are addition silicone, often shortened to a-silicone, and condensation silicone, often shorted to c-silicone. The two materials share many similarities but also some key differences that are essential to understand in order to best decide which one to use.
How Are They Similar?
Addition silicone and condensation silicone are both examples of elastic impression materials, more specifically synthetic elastomers. Synthetic elastomers are polymer-based impression materials which chemically cross-link when setting.
Both materials come as a putty or in a variety of viscosities that range from light body (also known as wash) to heavy body. A-silicone and c-silicone impressions can both be made using either a one-stage or two-stage technique.
One-stage impression
- Heavy body or putty is placed onto an impression tray. A layer wash is then placed over it or directly onto the relevant teeth or both. The impression tray is then placed back into the patient’s mouth for the material to set.
Two-stage impression
- A putty impression is recorded first, and after it has set it is relined with a thin layer of wash.
How Are Addition Silicone and Condensation Silicone Different?
The key difference between addition silicone and condensation silicone is in how they are formed. This is what gives the products their own unique advantages and disadvantages. As the names suggest, condensation silicone forms from a condensation chemical reaction while addition silicone forms from an addition chemical reaction. Though both products are created when a base paste mixes with an accelerator paste, the chemical reactions take place at different speeds and temperatures because of their different compositions.
Different Compositions
Addition Silicone
Base Paste:
- Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) - undergoes cross-linking
- Fillers (colloidal silica) - controls viscosity
- Colour pigments
Condensation Silicone
Base Paste:
- Polydimethyl siloxane - undergoes cross-linking
- Fillers (colloidal silica) - controls viscosity
- Colour pigments
Addition Silicone
Accelerator:
- Polyvinyl siloxane - cross-linking agent
- Platinum salt - catalyst
- Fillers - controls viscosity
Condensation Silicone
Accelerator:
- Alkyl silicate (orthosilicate) - cross-linking agent
- Stannous octoate - catalyst
- Fillers - controls viscosity
What are the advantages of addition silicone?
- Most dimensionally stable impression material
- Releases no by-products when set, so virtually no shrinkage
- Best fine detail
- Excellent stability allows multiple models to be made up at once
- Most time to pour (as long as 60 minutes after setting)
- Tasteless and no odour
- Best elastic recovery of all elastomers
- Adequate tear strength
- Hydrophobic – not susceptible to imbibition (swelling) or syneresis (shrinking)
- Short setting time (5-9 minutes) and adequate working time (2:15 minutes)
- Thixotropic (stays where you need it and flowable when you want it)
- Works better in high temperatures compared to c-silicone
What are the weaknesses of addition silicone?
- Higher priced versus alginate and condensation silicone
- Hydrophobic – excellent moisture control is required
- Inhibited by the sulphur in latex gloves and rubber dam, so non-latex gloves and dams should be used if necessary
- Susceptible to chemicals like nitrogen and phosphorus
- More technique sensitive versus c-silicone
What are the advantages of condensation silicone?
- More accurate than alginate
- High elasticity
- Adequate tear strength – better than addition silicone
- Adequate working time (2:30 seconds) and setting time (8-9 minutes)
- Hydrophobic – not susceptible to imbibition (swelling) or syneresis (shrinking)
- Tasteless and no odour
- Less messy than alginate
- Less expensive than a-silicone
- Biodegradable
What are the weaknesses of condensation silicone?
- Releases an alcohol by-product that can cause shrinkage
- Not as accurate as addition silicone
- Hydrophobic – excellent moisture control is required
- Higher priced than alginate
How to Decide Between Silicone Impression Materials
Both addition silicone and condensation silicone have unique characteristics that lend themselves to different clinical applications.
Though not able to record quite as fine a detail as addition silicone, condensation silicone can still give highly accurate results provided the working field is kept dry and the impression is poured within 30 minutes of being set.
Condensation silicone is the preferred choice for some dentists for its economy and adequate accuracy, however a-silicone has become the most used impression material in advanced restorative dentistry thanks to its unrivalled dimensional stability and fine detail reproduction.
How to Find the Right Brand of Silicone Impression Material
There are several different a-silicone and c-silicone brands currently on the market. Some of the most well-known include Affinis (from Coltene), Provil Novo (from Kulzer) and Honigum (from Zhermack).
Great value can also be found in own brand silicones, such as DEHP and Cybertech. These products offer near identical ranges and characteristics to the brands mentioned above, but usually at a lower price.
See our blog ‘How Cyber Silicone Compares to Honigum Impression Material’ for an example of how much money could be saved by choosing own brand silicone for your impressions.
Browse Own Brand Products
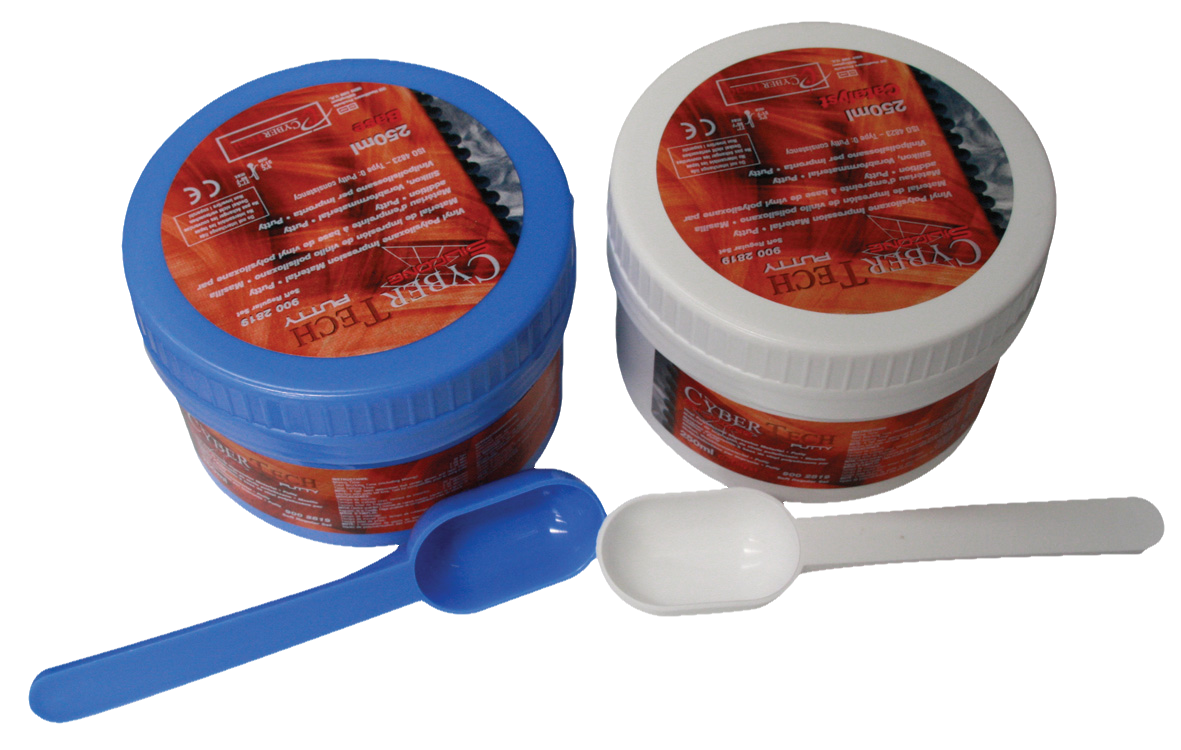

Cyber Silicone Putty Soft Regular 800g/500ml

Cyber Silicone Putty Soft Fast 800g/500ml

Cyber Silicone Wash Light Body Regular 50ml 4pk

Cyber Silicone Wash Light Body Fast 50ml 4pk

Cyber Silicone Wash Regular Body 50ml 4pk
Cyber Silicone Bite 50ml 4pk

DEHP C Silicone 2 Base 900ml