To make your scaling procedures as efficient and effective as they can be, it is important to understand the difference between different types of dental scalers and know what features to look out for. This includes knowing the difference between hand scaler designs, between sonic and ultrasonic devices and between magnetostrictive and piezoelectric devices.
Dental scalers are one of the most widely used instruments in dentistry. They are used primarily for removing plaque (calculus and tartar) and other deposits from the teeth, both above and below the gum line. The three types of scalers used in modern dentistry are hand scalers, sonic scalers and ultrasonic scalers.
Hand Scalers
Hand scaling is the most traditional method of removing plaque. Stainless-steel hand scalers are comprised of a handle and a tip. The tip is made up of a shank (upper and terminal) and a working end/blade. Most scalers now have tips at both ends of the handle.
Hand scalers with curved working ends are known as sickle scalers and are designed to be used on both anterior and posterior teeth. Scalers with no bend are known as straight scalers and are designed to be used on anterior teeth only.
Scaler tips come in several different designs for removing different levels of plaque. Thicker tips are more efficiency at removing heavier deposits while thinner tips are ideal for accessing difficult areas and tight tissues.
Most widely used hand scalers:
- H6/H7 Scaler - popular double-ended sickle scaler for use in the anterior, interproximal and premolar areas.
- 204 Scaler - sickle scaler for use in the posterior areas.
- M23 Scaler – universal scaler designed for interproximal access of anterior and posterior teeth.
Advantageous features to look out for:
- Silicone handle for a soft and firm grip.
- Lightweight/hollow design to help reduce hand fatigue.
- Premium quality stainless steel for better hardness, wear, corrosion resistance and less need for sharpening.
- Colour coding system to easily identify scaler type.
- Latex free to reduce the chances of an allergic reaction.
- Autoclavable to increase the lifespan of the scaler.
Kent Express Recommends – DEHP H6/H7 Scaler
Advantageous features to look out for:
- Silicone handle for a soft and firm grip.
- Lightweight/hollow design to help reduce hand fatigue.
- Premium quality stainless steel for better hardness, wear, corrosion resistance and less need for sharpening.
- Colour coding system to easily identify scaler type.
- Latex free to reduce the chances of an allergic reaction.
- Autoclavable to increase the lifespan of the scaler.
Kent Express Recommends – DEHP H6/H7 Scaler
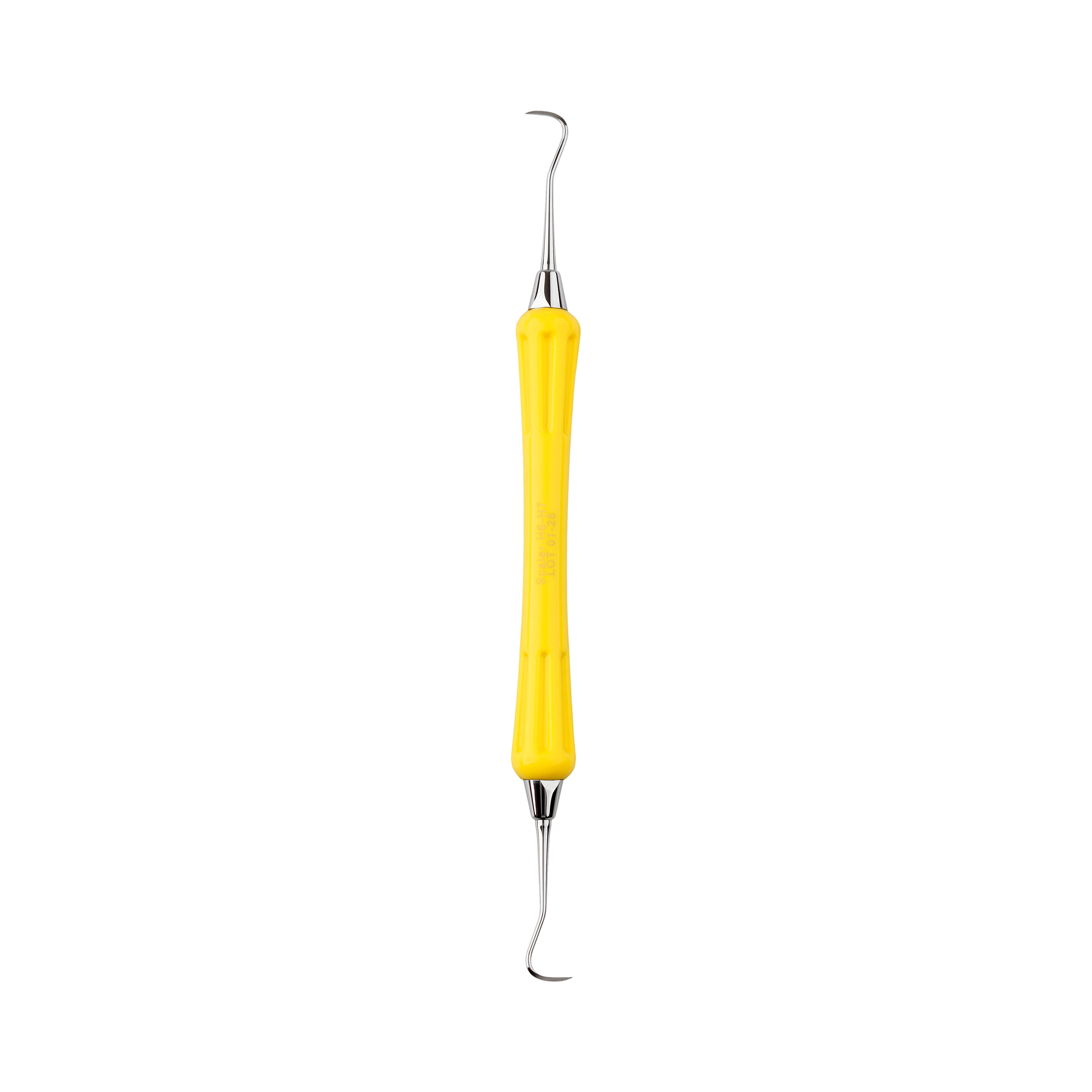

DEHP Scaler H6/H7 Silicone Handle Yellow
Sonic Scalers
Sonic scalers are electric, low power devices used for removing plaque and cleaning root surfaces. For heavy plaque, ultrasonic scalers are more effective. Similar in size and design to a dental handpiece, sonic scalers traditionally sit in the dental unit and are connected to a standard handpiece connector. Sometimes referred to as air scalers or scaler handpieces, sonic scalers are powered by an air-driven turbine that causes the tip to vibrate. Vibration occurs at approximately 3,000 - 8,000 cycles per second.
Advantageous features to look out for:
- A wide choice of tips for different clinical applications.
- Integrated spray.
- Slim and lightweight design for easier accessibility and user comfort.
- Fibre optics for improved visibility of the treatment site.
- Ability to easily adjust the power output.
Kent Express Recommends – BA Piezo Scaler w/Light with Handpiece & Tip
Advantageous features to look out for:
- A wide choice of tips for different clinical applications.
- Integrated spray.
- Slim and lightweight design for easier accessibility and user comfort.
- Fibre optics for improved visibility of the treatment site.
- Ability to easily adjust the power output.
Kent Express Recommends – BA Piezo Scaler w/Light with Handpiece & Tip
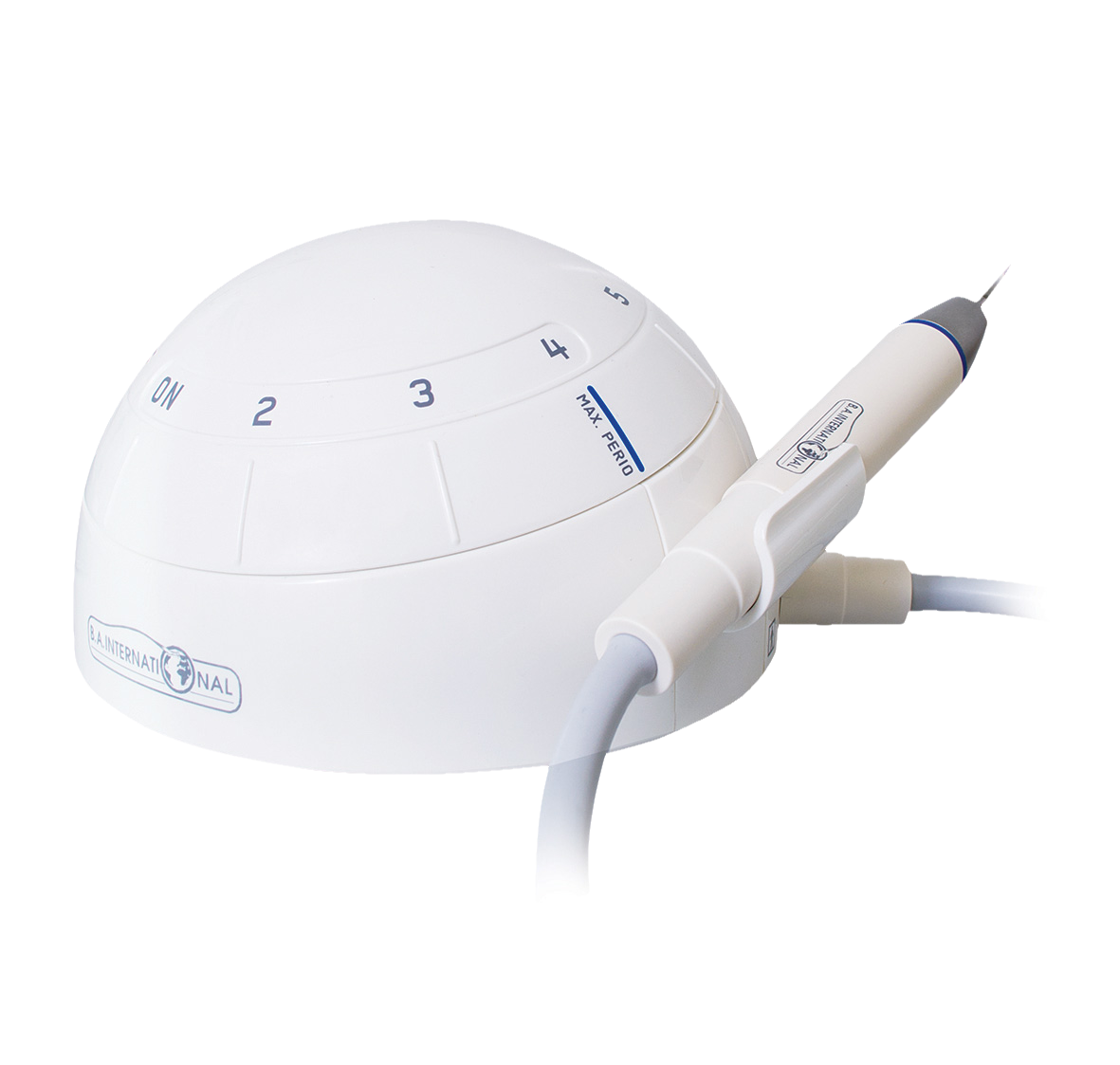

BA Piezo Scaler w/Light with Handpiece & Tip
For help finding the right scaler, speak to Michael our equipment specialist on 01634 877480.
Talk to our Expert
For help finding the right scaler, speak to Michael our equipment specialist on 01634 877480.

Talk to our Expert
For help finding the right scaler, speak to Michael our equipment specialist on 01634 877480.
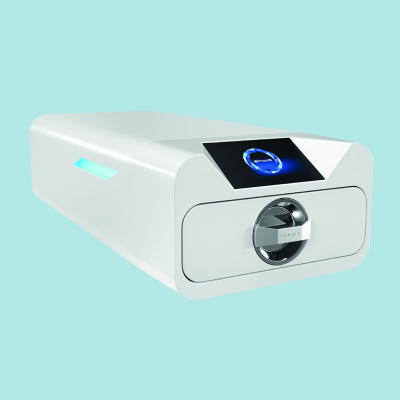
Ultrasonic Scalers
Ultrasonic scalers are electric, high frequency devices that connect to a compact and portable power unit that sits on the counter and plugs in at the wall. A water source must also be connected.
Similar in design to sonic scalers, ultrasonic scalers are more effective at removing heavy calculus and tartar. Vibration occurs at approximately 25,000 cycles per second or higher.
An additional benefit of ultrasonic scalers is cavitation. Cavitation is the formation of air bubbles in the water stream that break down and destroy the cells of harmful bacteria when they burst.

Ultrasonic scalers can be either magnetostrictive (i.e. Cavitron) or piezoelectric (i.e. Varios). The differences between the two are outlined in the table pictured.
Some hygienists prefer magnetostrictive scalers for their universal inserts and the fact that all sides of the magnetostrictive tip may be used for removing deposits, unlike the piezo tips which are designed specifically for that specific brand of scaler and only disperse power on the lateral sides.
Others might prefer piezo scalers for their wider and more ergonomic design and greater tactile sensitivity as the entire handpieces does not vibrate like magnetostrictive scalers do.
Though piezo and magnetostrictive designs each have passionate advocates, both do a fine job of calculus removal.
Advantageous features to look out for:
- Ergonomic design with lightweight cable
- 360 ° degrees rotating handpiece for convenient access
- Broad range of scaling inserts for different clinical applications
- Automatically adjusts to optimum frequency
- Fibre optics for improved visibility of the treatment site.
- Autoclavable components
- Different modes for general, perio and endo
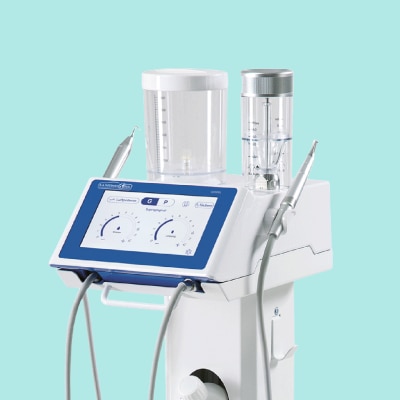
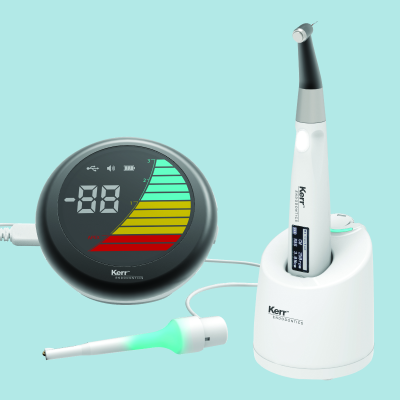
Kent Express Recommends – BA Ultimate UC500L Scaler and Air Polisher
Advantageous features to look out for:
- Ergonomic design with lightweight cable
- 360 ° degrees rotating handpiece for convenient access
- Broad range of scaling inserts for different clinical applications
- Automatically adjusts to optimum frequency
- Fibre optics for improved visibility of the treatment site.
- Autoclavable components
- Different modes for general, perio and endo
Kent Express Recommends – BA Ultimate UC500L Scaler and Air Polisher

BA Ulticlean UC500L Scaler and Air Polisher
What is the Best Dental Scaler?
Hand scalers, sonic scalers and ultrasonic scalers are all still commonly used in practice. Even hygienists who use electric scalers are likely to also have a hand scaler nearby as these can be just as effective at clearing plaque from easy to reach area of the mouth.
Dental hand scalers also require no plug in or hose connection making them a convenient option for removing minor plaque accumulation. Another advantage is the fact they don’t produce any aerosols. However, all this can come at a cost to the patient with hand scalers more likely to cause pain, discomfort and bleeding compared to electric scalers.
If the question was 'what the most effective dental scaler', the answer is undoubtedly ultrasonic scalers which is why most hygienist now use one. As well as being gentler on the gums and therefore easier for the patient to tolerate, ultrasonic scalers save time and remove hard plaque that neither hand scalers nor sonic scalers can.
The advantages that ultrasonic scalers provide over other scalers is reflected in price which needs to be factored in when purchasing. Ultimately, the decision comes down to budget and personal preference.