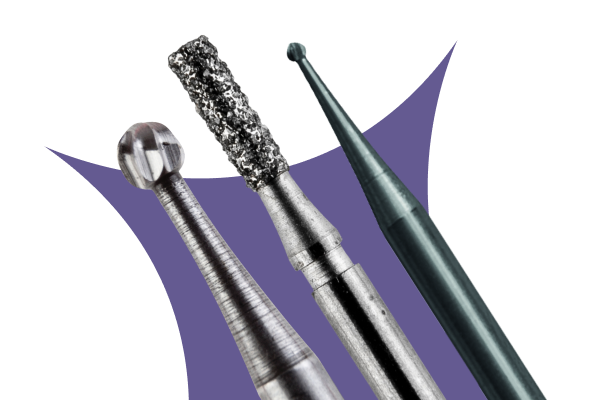
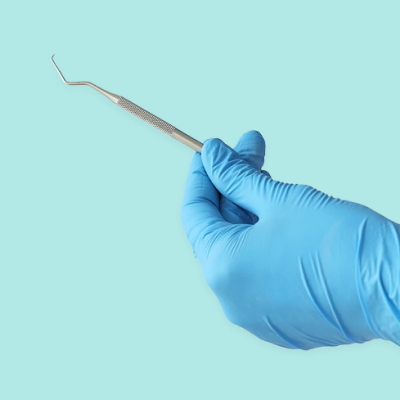
What Are Dental Burs?
Dental burs attach to a handpiece and are used for cutting and polishing hard tissues of the mouth. There’s a huge range available depending on the type of procedure that’s being undertaken. Typically they are made of steel, tungsten carbide or diamond grit.
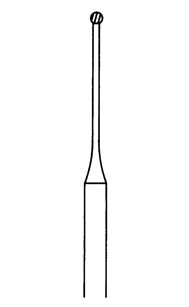
Burs have three parts: the head, the neck and the shank. The head contains blades which rotate to cut the tissue. The shank is the longest part and is inserted into the handpiece. The neck connects the two parts. The angle and positioning of the blades and the shape of the head determines the bur’s use.
Diamond Burs
Diamond burs (ISO 806) are widely used by dentists around the world, most often with high speed handpieces. Diamond is able to grind away hard tissues such as enamel and bone, leaving a rough surface. They are formed by bonding small particles of diamond onto a substrate. Most commonly they come with a friction grip (FG) shank. They’re designed to reduce tooth structures and are commonly used for crown and veneer related procedures. High quality, they offer tremendous accuracy, allowing a fast and smooth cut. However they tend to have a shorter lifespan than other types of burs; repeated sterilisation reduces their cutting effectiveness.
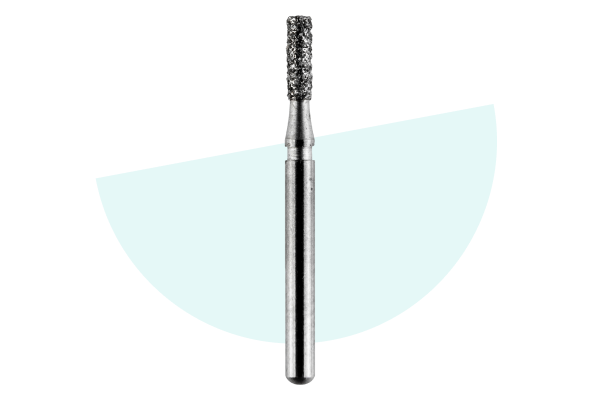

DEHP Diamond Burs
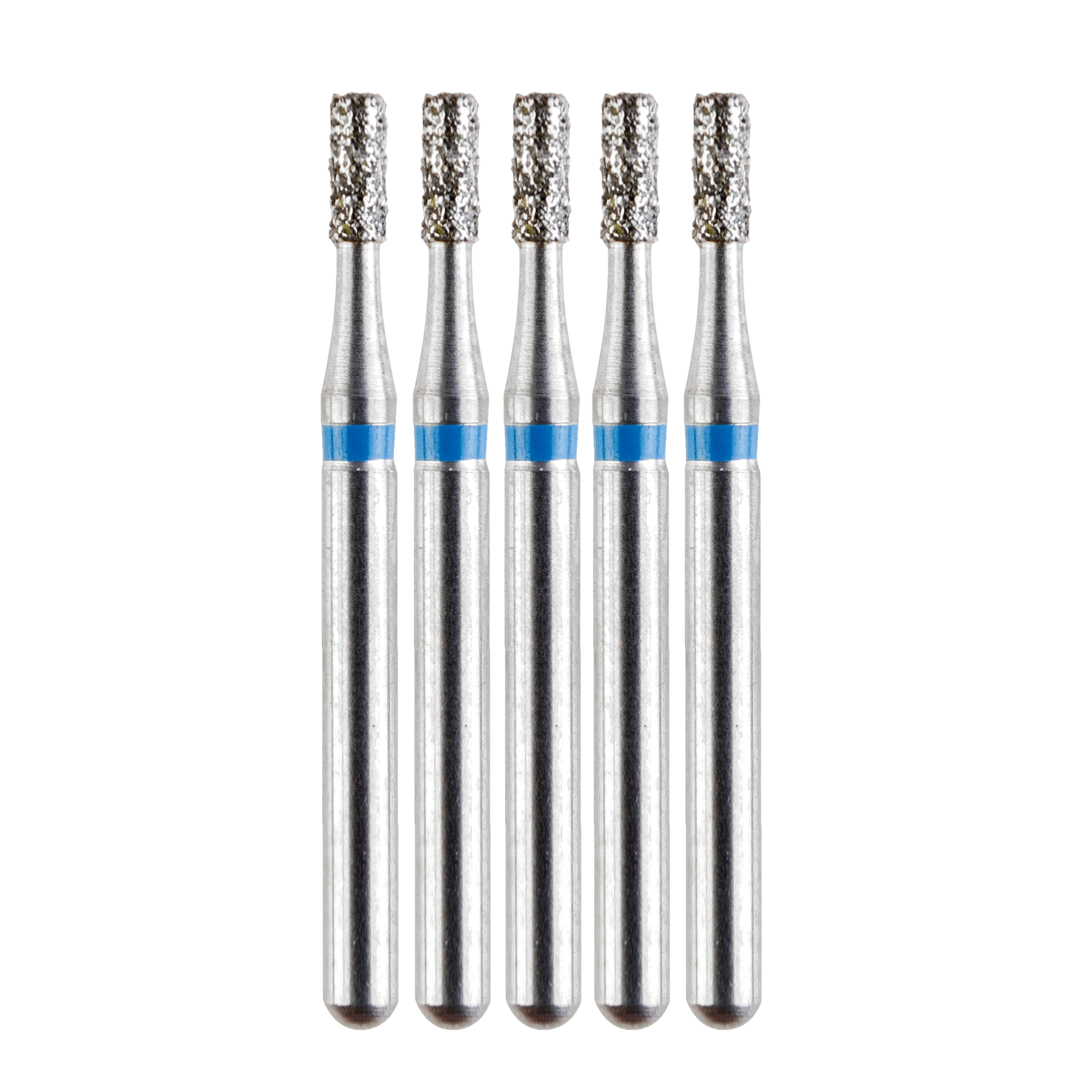

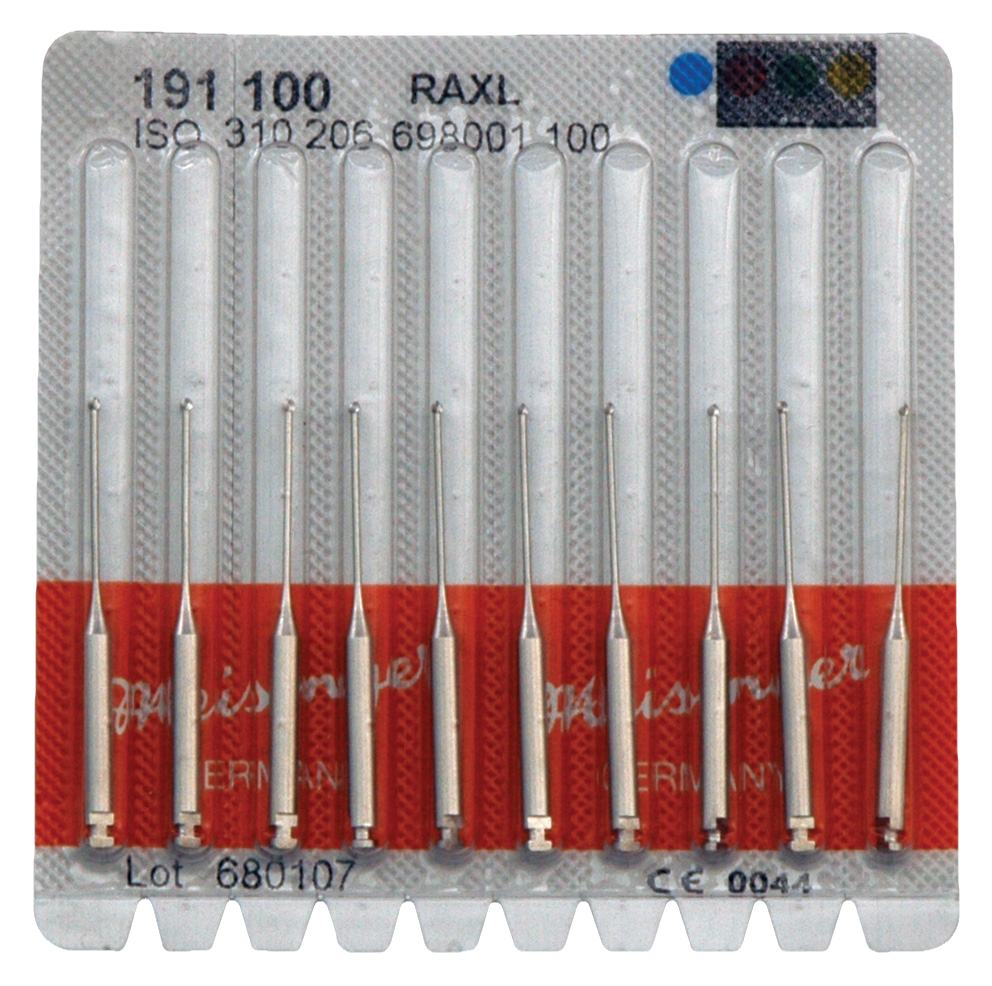
DEHP Bur Diamond FG 108-011 M (835) Flat End Cylinder 541 5pk
DEHP Diamond Burs
DEHP Diamond Burs are made from the finest quality diamonds and the shank is hardened, ground 420F grade stainless steel. Concentric, balanced and ISO colour coded for quick grit identification

DEHP Bur Diamond FG 108-011 M (835) Flat End Cylinder 541 5pk
Tungsten Carbide Burs
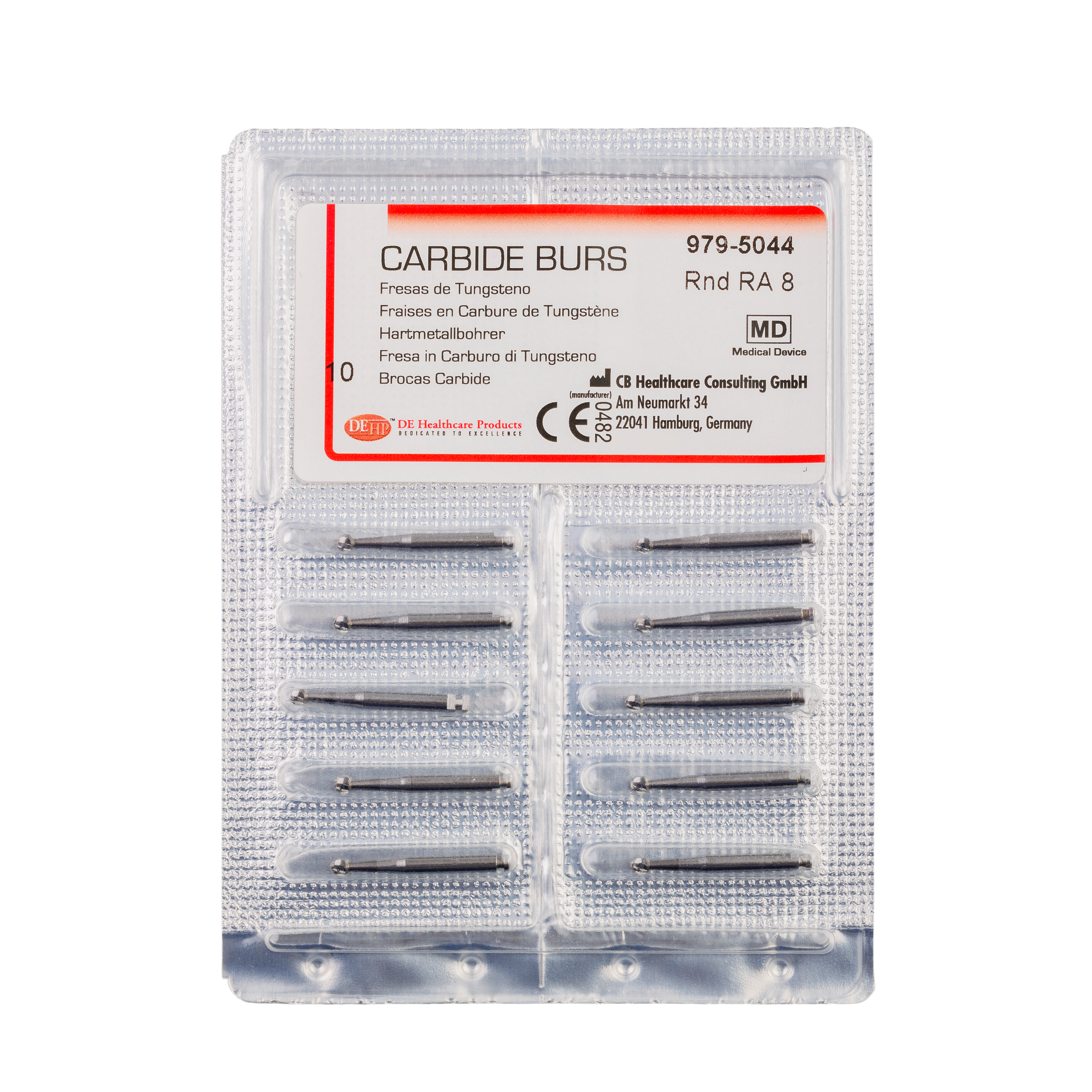
DEHP Bur TC RA Round 8 (023) 10pk
Tungsten Carbide Burs
Tungsten Carbide burs (ISO 500) are also known for their excellent precision. Tungsten carbide burs are three times harder than steel and this alloy helps the dentist to smooth down tooth structures to an incredible finish. They are available with FG and RA shanks. They’re often used when trimming and finishing composite restorations. They’re higher priced than steel burs, but they compensate for this with a longer working life. They are known for their minimal vibration and ‘chatter’ compared to other types of dental burs, and tend to build up little debris in use.
Often a tungsten carbide bur actually only has carbide in the tip; the material is brittle compared to steel, so often the shank will still be made of steel.

DEHP Bur TC RA Round 8 (023) 10pk
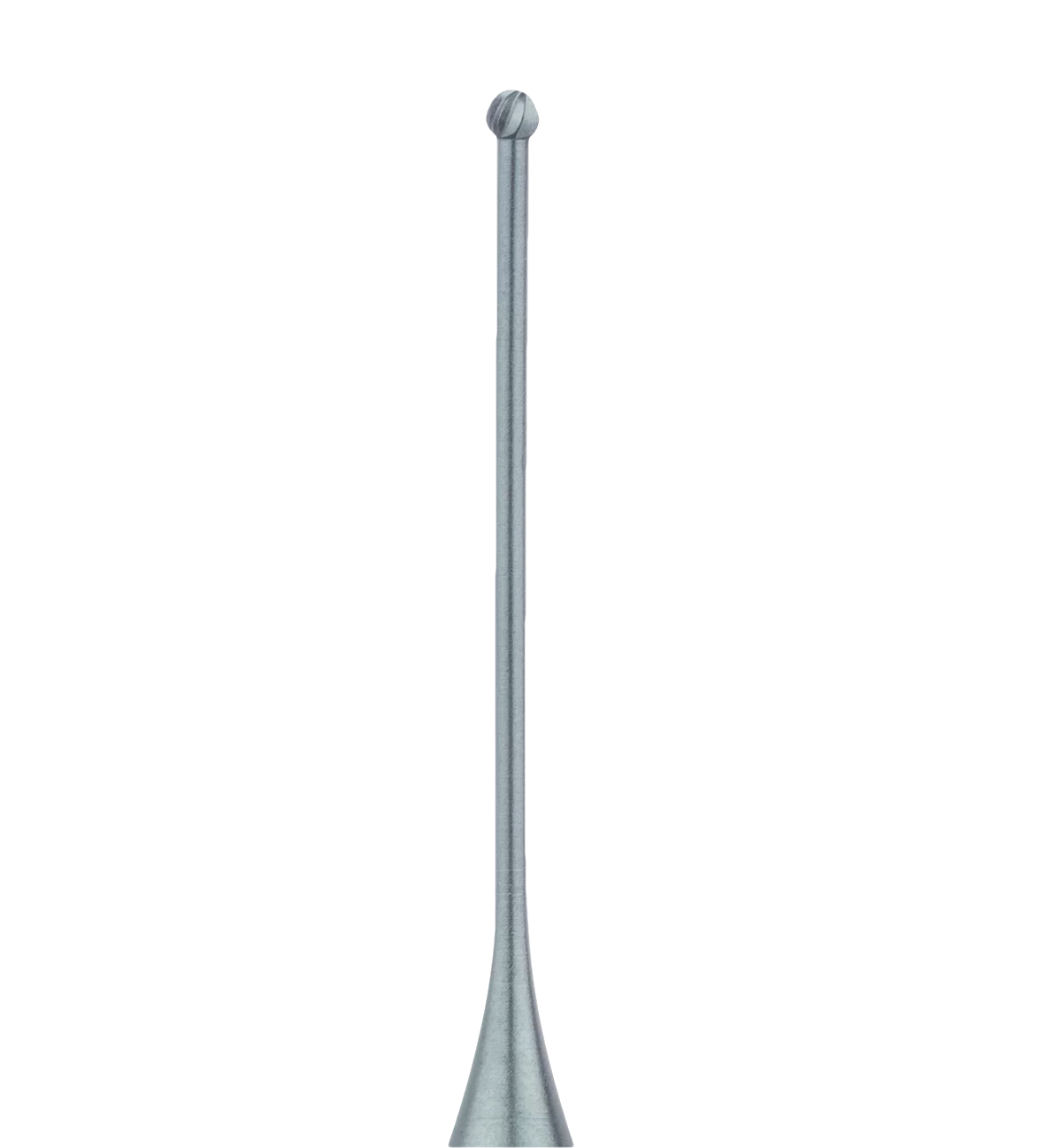
HP or "handpiece" burs
HP or “handpiece†burs are the larger, long straight shank types with a shank diameter of 2.35mm. The length is defined by ISO numbers starting with 1XX. This particular type of bur is used on slow speed handpieces and are even used in surgery procedures as well as the reduction of the smaller cheek teeth.

FG or "friction grip" burs
FG or “friction grip” burs are used by dentists when working with high speed handpieces. They possess a smooth shaft and the length of the handle is defined by ISO numbers starting with 3XX. Typically they are around 20mm in length and 1.6mm in diameter.

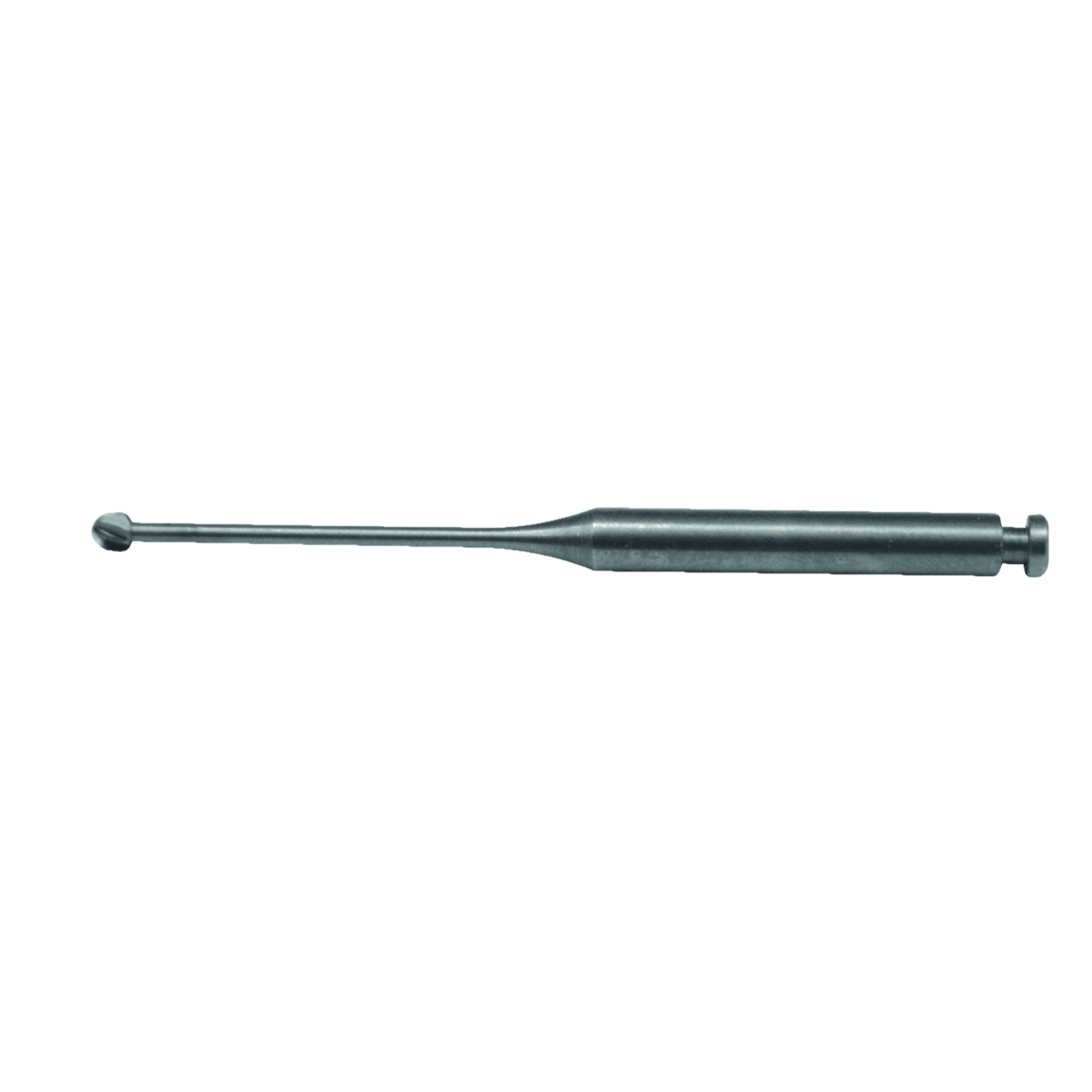
RA or "right angle" burs
RA or “right angle†burs latch on to low speed contra-angle handpieces with a notch at the end of the handle. Again they have a shaft diameter of 2.35mm and the length is defined by ISO codes starting with 2XX. They’re available with the same shapes as FG shanks.
In general, round and pear burs are used for cavity preparation and undercuts, cross-cut burs are used for crown work and sectioning multi-rooted teeth, and finishing burs are used for finishing restorations.
Dental Burs From Kent Express
Kent Express offers a wide range of burs from all leading manufacturers, and we encourage you to take advantage of our easy online ordering service. Our dedicated, experienced account managers are on hand to offer free advice and answer any questions you may have on 0800 028 1181. Lines are open between 8.30am and 5.30pm and we would love to hear from you today.